BLOG
Government Schemes and Initiatives for Start Up Businesses
Aug 8 2016
Darren Best

 Photo Credit: Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock
Photo Credit: Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock
The Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS)
What is SEIS? With the SEIS you can invest as much as £100,000 in any tax year. In return, the Government provides income tax relief up to the value of 50% of the money invested. So for instance, if you invested £100,000 the Government would provide you with an income tax relief of £50,000 (£100,000 x 50%). This significantly means that 50% of the risk associated with the investment is taken away. If the business succeeds and you make a profit on the sale of your shares, you will be exempt from any capital gains tax on that profit. In the unfortunate case the start up business fails the loss is tax deductible, meaning you may be able to offset your loss against your income tax. Through the SEIS, the government is seeking to reduce the damage limitation on an investment that goes wrong and enriching the return on an investment that goes right. Main Qualifying Criteria for SEIS Eligibility: - Must be independent and unquoted - Fewer than 25 full time employees - No venture capital investment in place - Trading for less than two years - Gross assets of less than £200,000 before share issue/at point of investment - Preparing to or undertaking a permitted “qualifying trade” (non-qualifying trades exemptions list can be found at HM Revenue and Customs) - Maximum shareholding in the business no more than 30%The Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS)
What is EIS? If you are a private investor living and paying tax in the UK, you can invest between £2,000 and £1 million pounds in an EIS in any tax year. In return the HMRC give you a 30% tax rebate on your investment, which is claimable against the tax you paid in the last tax year or tax you have paid or still owe in the current tax year. This in essence transfers 30% of the risk inherent in the investment to the Government. If the start up business succeeds and you make a profit on the sell of your shares, then you will be also exempt from capital gains tax on that profit. If you have a capital gains or inheritance tax liability to pay in the current tax year or have paid any of these taxes in the last two to three years, you can claw back or defer tax equivalent to 28% on the capital you have invested in the EIS start up business. This would effectively transfer 58% of your investment risk to the UK government. In the scenario the start up business fails, you can also offset your loses against your income. Through the scheme, the Government is fundamentally making it easier for private investors to invest in start up businesses that can qualify to participate in EIS. Main Qualifying Criteria for EIS Eligibility: - Must be independent and unquoted - Gross assets of less than £15 million before share issue/at point of investment - Fewer than 250 full time employees - Preparing to or undertaking a permitted “qualifying trade” (non-qualifying trades exemptions list can be found at HM Revenue and Customs) - Maximum shareholding in the business no more than 30%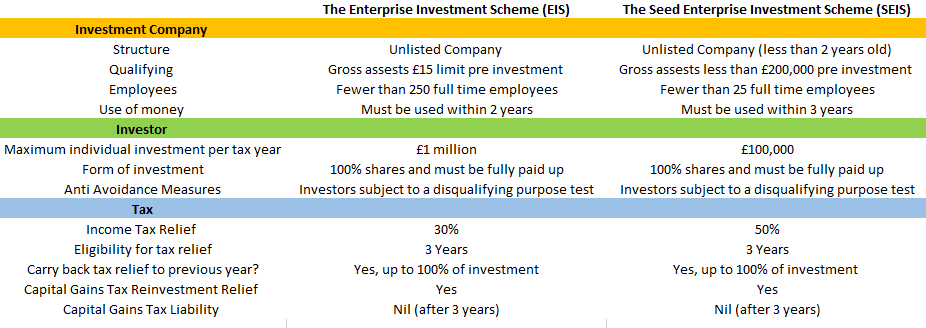
Research and Development Initiatives for Start Up Businesses
Whilst the focus thus far has been on tax scheme based government support for start up businesses, the ‘Research & Development (R&D) Tax Credits’ and the ‘Patent Box Relief’ initiatives allow start up businesses to gain benefits from their qualifying R&D activities.
Photo credit: Constantin Stanciu/Shutterstock
The Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credits
What are R&D Tax Credits? Innovation is a vital component to any economy’s growth, productivity and competitiveness. In the UK, any businesses actively seeking to enhance processes (such as production) through an advance in science or technology or both may be eligible for R&D tax credits. Currently, the Government offer two R&D tax credit systems, one for SME’s and another for large companies. For the purposes of this piece, the focus will be upon the SME R&D tax credit regime. The current R&D tax claim enhancement (the enhanced deduction) is 230% of the qualifying R&D expenditure incurred. If an SME brings expenditure of £100,000 on qualifying R&D, it can deduct £230,000 when working out its taxable profit or loss. As the £100,000 would already be accounted for in its accounts, the balance of £130,000 (£230,000 - £100,000) would be an additional deduction from its taxable profit. The corporation tax (at a rate of 20%) would be £26,000 (£130,000 x 20%). That’s the equivalent of your business getting 26p from HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) for every £1 spent on R&D activities. Main Qualifying Criteria for SME R&D Tax Credits Eligibility: - Fewer than 500 employees - Turnover of less than €100m, or - Gross assets less than €86m - Seek to overcome technological uncertainties - Aim to achieve an advance in technology which isn’t readily deducible by a competent professional - Use some kind of science i.e. data science - Have an element of business risk or uncertainty
The Patent Box Relief
Principally, the aim of the patent box relief is to encourage businesses to retain and commercialise patents and develop new innovative patented products in the UK. The influence of the patent box relief is to reduce the effective rate of corporation tax on qualifying profits attributed to patented products and similar intellectual property (IP) for more than 20% to just 10% (current rate 11%, 10% rate applicable from 2017/18). The patent box relief means for any business that pays corporation tax in the UK, in the future there will be a financial benefit on owning patents on products and IP that contribute towards the businesses profits. If your business continually develops new products and pay’s corporation tax, then you should be seriously considering whether you could gain patent protection. In doing so, your corporation tax liability could notably be reduced. When considering the patent box relief initiative, it is important not to make the assumption that only pioneering new products or technology can be patented. Most patented creations are cumulative advances on prior or existing knowledge. Main Qualifying Criteria for Patent Box Relief Eligibility: - Must be subject to UK corporation tax - Must not hold a qualifying IP right or hold an exclusive license over it - Must not be an individual, partnership or a limited liability partnership (LLP) - No secret patents in place - Business genuinely must significantly contribute towards the creation and innovation of the protected item(s)